Page 17 - The Basics IA by ETron Circuit Labs
P. 17
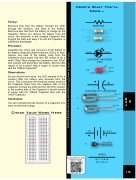
Theory:Electrons flow from the battery, through the LED, through the resistors, and back to the battery. Electrons also flow from the battery to charge up the Capacitor. When you remove the battery from the circuit, the electrons in the charged Capacitor flow through the LED and keep it lit until the Capacitor is sufficiently discharged.Procedure:Assemble the circuit and connect a 9-volt battery to the Battery Snap and observe that the LED is lit. Now, remove one lead of the battery snap from the solderless circuit board. Did the LED remain lit for a while? Why? Now change the Capacitor to the 100uF and connect and disconnect the battery. Did the LED remain lit for a while? Was it longer or shorter than with the 1000uF Capacitor?Observations:As you should have seen, the LED remains lit for a moment after the battery was removed from the circuit. This is because the electrical energy stored in the Capacitor flows from the negative side of the Capacitor through the LED and the 330 Ohm resistor to the positive side of the Capacitor It should remain lit longer with the 1000uF Capacitor than with the 100uF Capacitor.Conclusion:You can conclude that the function of a Capacitor is to store an electrical charge.Check Your Work Here a b c d e 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 a b c d e f g h i j 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 f g h i j Here’s What You’ll Need...hole 4cRESISTORR1R2hole 17bhole 30b1K $ (Brown, Black, Red, Gold) hole 17c330 Ohm ' (Orange, Orange, Brown, Gold) Anode CathodeLIGHT EMITTING DIODE (LED)LED 1Cathode (flat side)hole 4e hole 4fC1C11000uF100uFhole 17dhole 17hhole 17dhole 17hELECTROLYTIC CAPACITORSREDB1WIRESW1 = 17j & 30j W2 = 4i & 17iBLACKred = hole 30e black = hole 30hSCAN HERE TO SEE MORE ONLINE1X5XAnodeLAB 8Visit us online at www.ETronCircuit.com for more exciting projects